
|

|
Forum Index : Microcontroller and PC projects : ESP8266 Neopixel ntp-sourced clock
| Author | Message | ||||
| matherp Guru Joined: 11/12/2012 Location: United KingdomPosts: 10953 |
Something completely different  Behind dark smoked perspex 7:17:38 Development environment 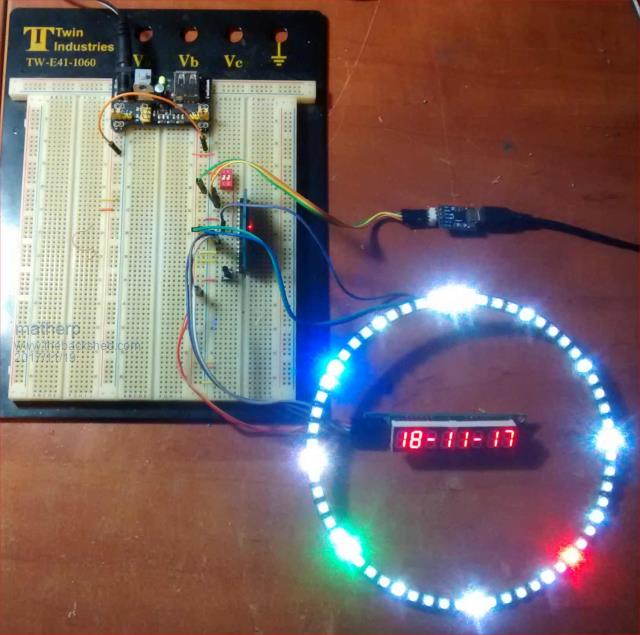 This little development uses an ESP8266 programmed with the Arduino IDE. The ESP8266 connects to my WIFI and downloads the current time and date from an ntp server every 10 minutes. In between the time is updated on the NEOPIXEL ring from the ESP's crystal oscillator. Red is the seconds, blue the minutes and green the hours. The clock automatically compensates for daylight saving. The Date is shown using a MAX7219 7-segment LCD display Getting the ESP8266 up and running with the Arduino IDE is simple - just google. I then use a standard USB/UASRT to program the ESP. As always with the ESP GPIO0 must be connected to GND to program and then the chip RESET. The code is attached. It is currently somewhat UK/Europe specific in terms of the summertime calculation but this is easily modified. #include <ESP8266WiFi.h> #include <WiFiUdp.h> #include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h> #include <time.h> // // Local set up, DST flexibility NOT YET IMPLEMENTED IN CODE // #define timezone 0 //specify the offset in minutes +/- from GMT #define hemisphere 0 //specify northern (0) or southern hemisphere (1) #define ntpfrequency 10 //specify minutes between ntp updates #define DSTstartSunday 0 //specify which Sunday to start daylight saving (use 0 for last Sunday) #define DSTendSunday 0 //specify which Sunday to end daylight saving (use 0 for last Sunday) #define DSTstartmonth 3 //specify month to start daylight savings (1-12) #define DSTendmonth 10 //specify month to start daylight savings (1-12) const char* ntpServerName = "3.uk.pool.ntp.org"; char ssid[] = "yourSSID"; // your network SSID (name) char pass[] = "yourPASSWORDr"; // your network password // // Which pin on the ESP8266 is connected to the NeoPixels? #define PIN 2 // How many NeoPixels are attached to the ESP8266? #define NUMPIXELS 60 // When we setup the NeoPixel library, we tell it how many pixels, and which pin to use to send signals. Adafruit_NeoPixel pixels = Adafruit_NeoPixel(NUMPIXELS, PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800); unsigned int localPort = 2390; // local port to listen for UDP packets /* Don't hardwire the IP address or we won't get the benefits of the pool. * Lookup the IP address for the host name instead */ IPAddress timeServerIP; // NTP server address const int NTP_PACKET_SIZE = 48; // NTP time stamp is in the first 48 bytes of the message unsigned long currentMillis,previousMillis=0; byte packetBuffer[ NTP_PACKET_SIZE]; //buffer to hold incoming and outgoing packets int interval=1000; int lit=NUMPIXELS-1; #define YEAR0 1900 /* the first year */ #define EPOCH_YR 1970 /* EPOCH = Jan 1 1970 00:00:00 */ #define SECS_DAY (24L * 60L * 60L) #define LEAPYEAR(year) (!((year) % 4) && (((year) % 100) || !((year) % 400))) #define YEARSIZE(year) (LEAPYEAR(year) ? 366 : 365) #define FIRSTSUNDAY(timp) (((timp)->tm_yday - (timp)->tm_wday + 420) % 7) #define FIRSTDAYOF(timp) (((timp)->tm_wday - (timp)->tm_yday + 420) % 7) #define TIME_MAX ULONG_MAX #define ABB_LEN 3 #define MAX_CS 12 #define MAX_CLK 14 #define MAX_DO 13 // A UDP instance to let us send and receive packets over UDP WiFiUDP udp; const uint8_t MAXch[10]={0x7E, 0x30, 0x6D, 0x79, 0x33, 0x5B, 0x5F, 0x70, 0x7F, 0x7B}; const int _ytab[2][12] = { { 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 }, { 31, 29, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 } }; /* Number of days per month (except for February in leap years). */ static const int monoff[] = { 0, 31, 59, 90, 120, 151, 181, 212, 243, 273, 304, 334 }; static int is_leap_year(int year) { return year % 4 == 0 && (year % 100 != 0 || year % 400 == 0); } static int leap_days(int y1, int y2) { --y1; --y2; return (y2/4 - y1/4) - (y2/100 - y1/100) + (y2/400 - y1/400); } time_t timegm(const struct tm *tm) { int year; time_t days; time_t hours; time_t minutes; time_t seconds; year = 1900 + tm->tm_year; days = 365 * (year - EPOCH_YR) + leap_days(EPOCH_YR, year); days += monoff[tm->tm_mon]; if (tm->tm_mon > 1 && is_leap_year(year)) ++days; days += tm->tm_mday - 1; hours = days * 24 + tm->tm_hour; minutes = hours * 60 + tm->tm_min; seconds = minutes * 60 + tm->tm_sec; return seconds; } struct tm * gmtime(const time_t *timer) { static struct tm br_time; struct tm *timep = &br_time; time_t time = *timer; unsigned long dayclock, dayno; int year = EPOCH_YR; dayclock = (unsigned long)time % SECS_DAY; dayno = (unsigned long)time / SECS_DAY; timep->tm_sec = dayclock % 60; timep->tm_min = (dayclock % 3600) / 60; timep->tm_hour = dayclock / 3600; timep->tm_wday = (dayno + 4) % 7; /* day 0 was a thursday */ while (dayno >= YEARSIZE(year)) { dayno -= YEARSIZE(year); year++; } timep->tm_year = year - YEAR0; timep->tm_yday = dayno; timep->tm_mon = 0; while (dayno >= _ytab[LEAPYEAR(year)][timep->tm_mon]) { dayno -= _ytab[LEAPYEAR(year)][timep->tm_mon]; timep->tm_mon++; } timep->tm_mday = dayno + 1; timep->tm_isdst = 0; return timep; } void sendcommand(uint16_t MAXregister, uint16_t command){ uint16_t tosend=(MAXregister<<8) + command; for(int i=0; i<16; i++) // There are 16 bits in a command { digitalWrite(MAX_DO, bitRead(tosend, 15-i)); // Set MOSI delayMicroseconds(5); digitalWrite(MAX_CLK, HIGH); // SCK high delayMicroseconds(5); digitalWrite(MAX_CLK, LOW); // SCK low delayMicroseconds(5); } digitalWrite(MAX_CS,HIGH); delayMicroseconds(50); digitalWrite(MAX_CS,LOW); } // MAX7219 Registers #define MAXdecode 0x09 #define intens 0x0A #define scanlim 0x0B #define Shutdwn 0x0C #define DigTest 0x0F #define Init_Inten 0x0f #define No_Digits 7 #define Set_On 1 #define Set_Off 0 void initmax7219(void){ pinMode(MAX_CS, OUTPUT); pinMode(MAX_CLK, OUTPUT); pinMode(MAX_DO, OUTPUT); digitalWrite(MAX_CS, LOW); digitalWrite(MAX_CLK, LOW); delay(10); sendcommand(MAXdecode,0); //we want straight access to the elements of the LEDs sendcommand(intens,Init_Inten); sendcommand(scanlim,No_Digits); sendcommand(Shutdwn, Set_On); sendcommand(DigTest, Set_Off); for(int i=1; i<=8; i++){ sendcommand(i,0); } } void setup() { initmax7219(); pixels.begin(); // This initializes the NeoPixel library. for(int i=0;i<NUMPIXELS;i++){ pixels.setPixelColor(i, pixels.Color(0,0,0)); } pixels.show(); Serial.begin(115200); Serial.println(); Serial.println(); // We start by connecting to a WiFi network Serial.print("Connecting to "); Serial.println(ssid); WiFi.begin(ssid, pass); while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) { delay(500); Serial.print("."); } Serial.println(""); Serial.println("WiFi connected"); Serial.println("IP address: "); Serial.println(WiFi.localIP()); Serial.println("Starting UDP"); udp.begin(localPort); Serial.print("Local port: "); Serial.println(udp.localPort()); } int summertimeUK(unsigned long epoch){ struct tm *sos; struct tm stma; sos=&stma; struct tm *eos; struct tm etma; eos=&etma; struct tm *now; struct tm snow; now=&snow; int sundaycount=0; int dayofmonth=31; time_t sostimestamp, eostimestamp; now=gmtime((const time_t*)&epoch); do { sos->tm_year = now->tm_year; sos->tm_mon = 2; sos->tm_mday = dayofmonth; sos->tm_hour = 1; sos->tm_min = 0; sos->tm_sec = 0; sostimestamp = timegm(sos); sos=gmtime(&sostimestamp); if(sos->tm_wday==0)sundaycount=1; dayofmonth--; } while(!sundaycount); sundaycount=0; dayofmonth=31; do { eos->tm_year = now->tm_year; eos->tm_mon = 9; eos->tm_mday = dayofmonth; eos->tm_hour = 1; eos->tm_min = 0; eos->tm_sec = 0; eostimestamp = timegm(eos); eos=gmtime(&eostimestamp); if(eos->tm_wday==0)sundaycount=1; dayofmonth--; } while( !sundaycount); if(epoch<sostimestamp || epoch>eostimestamp){ return 0; } else { return 1; } } void printdatetime(const struct tm *tm){ Serial.print(tm->tm_mday); Serial.print('-'); if ( tm->tm_mon < 9 ) { // In the first 10 minutes of each hour, we'll want a leading '0' Serial.print('0'); } Serial.print(tm->tm_mon+1); Serial.print('-'); Serial.print(tm->tm_year % 100); Serial.print(' '); Serial.print(tm->tm_hour); // print the hour (86400 equals secs per day) Serial.print(':'); if ( tm->tm_min < 10 ) { // In the first 10 minutes of each hour, we'll want a leading '0' Serial.print('0'); } Serial.print(tm->tm_min); // print the minute (3600 equals secs per minute) Serial.print(':'); if ( tm->tm_sec < 10 ) { // In the first 10 seconds of each minute, we'll want a leading '0' Serial.print('0'); } Serial.println(tm->tm_sec); // print the second sendcommand(8,MAXch[tm->tm_mday / 10]); sendcommand(7,MAXch[tm->tm_mday % 10]); sendcommand(5,MAXch[(tm->tm_mon+1) / 10]); sendcommand(4,MAXch[(tm->tm_mon+1) % 10]); sendcommand(2,MAXch[(tm->tm_year % 100) / 10]); sendcommand(1,MAXch[tm->tm_year % 10]); // sendcommand(8,MAXch[tm->tm_hour / 10]); // sendcommand(7,MAXch[tm->tm_hour % 10]); // sendcommand(5,MAXch[tm->tm_min / 10]); // sendcommand(4,MAXch[tm->tm_min % 10]); // sendcommand(2,MAXch[tm->tm_sec / 10]); // sendcommand(1,MAXch[tm->tm_sec % 10]); sendcommand(3,1); sendcommand(6,1); } void loop() { int done=0; unsigned long epoch, DST; struct tm *tm; struct tm tma; tm=&tma; //get a random server from the pool WiFi.hostByName(ntpServerName, timeServerIP); sendNTPpacket(timeServerIP); // send an NTP packet to a time server // wait to see if a reply is available delay(900); int cb = udp.parsePacket(); if (!cb) { Serial.println("no packet yet"); done=ntpfrequency*60-10; //try again in 10 seconds } else { Serial.print("packet received, length="); Serial.println(cb); // We've received a packet, read the data from it udp.read(packetBuffer, NTP_PACKET_SIZE); // read the packet into the buffer //the timestamp starts at byte 40 of the received packet and is four bytes, // or two words, long. First, esxtract the two words: unsigned long highWord = word(packetBuffer[40], packetBuffer[41]); unsigned long lowWord = word(packetBuffer[42], packetBuffer[43]); // combine the four bytes (two words) into a long integer // this is NTP time (seconds since Jan 1 1900): unsigned long secsSince1900 = highWord << 16 | lowWord; Serial.print("Seconds since Jan 1 1900 = " ); Serial.println(secsSince1900); epoch=secsSince1900-2208988800UL; tm=gmtime((const time_t*)&epoch); // print the hour, minute and second: Serial.print("The UTC time is "); // UTC is the time at Greenwich Meridian (GMT) printdatetime(tm); } // wait six hundred seconds before asking for the time again do { int hourpos; ESP.wdtFeed(); currentMillis = millis(); if ((unsigned long)(currentMillis - previousMillis) >= interval) { previousMillis = currentMillis; // It's time to do something! // Use the snapshot to set track time until next event if(done)epoch++; DST=epoch; DST+=(timezone*60); if(summertimeUK(DST)) DST+=3600; tm=gmtime((const time_t*)&DST); for(int i=0;i<NUMPIXELS;i++){ pixels.setPixelColor(i, pixels.Color(1,1,1)); if(!(i % 5))pixels.setPixelColor(i, pixels.Color(10,10,10)); } for(int i=0;i<NUMPIXELS;i+=15){ pixels.setPixelColor(i, pixels.Color(70,70,70)); } pixels.setPixelColor(59, pixels.Color(30,30,30)); pixels.setPixelColor(1, pixels.Color(30,30,30)); hourpos=(tm->tm_hour % 12) * 5 + (tm->tm_min / 12); pixels.setPixelColor(tm->tm_sec, pixels.Color(170,0,0)); pixels.setPixelColor(tm->tm_min, pixels.Color(0,0,255)); pixels.setPixelColor(hourpos, pixels.Color(0,170,0)); if(tm->tm_sec==tm->tm_min)pixels.setPixelColor(tm->tm_min, pixels.Color(170,0,255)); if(tm->tm_min==hourpos)pixels.setPixelColor(hourpos, pixels.Color(0,170,255)); if(tm->tm_sec==hourpos)pixels.setPixelColor(hourpos, pixels.Color(170,170,0)); if(tm->tm_sec==tm->tm_min && tm->tm_min==hourpos)pixels.setPixelColor(hourpos, pixels.Color(170,170,255)); pixels.show(); done++; printdatetime(tm); delay(900); } } while(done<ntpfrequency*60); done=0; } // send an NTP request to the time server at the given address unsigned long sendNTPpacket(IPAddress& address) { Serial.println("sending NTP packet..."); // set all bytes in the buffer to 0 memset(packetBuffer, 0, NTP_PACKET_SIZE); // Initialize values needed to form NTP request // (see URL above for details on the packets) packetBuffer[0] = 0b11100011; // LI, Version, Mode packetBuffer[1] = 0; // Stratum, or type of clock packetBuffer[2] = 6; // Polling Interval packetBuffer[3] = 0xEC; // Peer Clock Precision // 8 bytes of zero for Root Delay & Root Dispersion packetBuffer[12] = 49; packetBuffer[13] = 0x4E; packetBuffer[14] = 49; packetBuffer[15] = 52; // all NTP fields have been given values, now // you can send a packet requesting a timestamp: udp.beginPacket(address, 123); //NTP requests are to port 123 udp.write(packetBuffer, NTP_PACKET_SIZE); udp.endPacket(); } |
||||
| djuqa Guru Joined: 23/11/2011 Location: AustraliaPosts: 447 |
Great stuff I have also gone over to the darkside (aka ARDUINO ide/ESP8266) With ESP8266 (Including Arduino formfactor) modules so cheap, yet so capable of doing amazing things. Now bought several esp8266 & Arduino boards less than third of the price of the 2 Explore64 kits I killed trying to solder the MONGREL SMD PIC32 MCU. VK4MU MicroController Units |
||||
| cheeseprader Newbie Joined: 06/10/2016 Location: United StatesPosts: 7 |
This would be a great project/program for a 28 pin micromite using a DS3231 module. I think I saw someone using ws2812s or APA102s, and the MAX7219 module on the tbs forum. Might have to do a search... You could use one of those I2C adafruit 7 segment displays too I guess with the circular led display. Another great project Matherp! |
||||
| WhiteWizzard Guru Joined: 05/04/2013 Location: United KingdomPosts: 2960 |
That NeoPixel ring is brilliant - never seen them as a 'clock design' before (i.e. with a suitable quantity of LEDs). I have a 44pin MKI Micromite (MX150) that has been running a 40x8 red led matrix digital GPS clock for over 3years now. My children are just starting to understand how to read analogue time so I wanted to somehow 'retro-fit' an analogue feature to the matrix clock. So that 'ring' is the perfect addition but I will definitely be doing it as 'cheeseprader' suggests; i.e. for a MM rather than the ESP. THANKS for sharing this brilliantly simple design idea. WW |
||||
| zoggermaster Newbie Joined: 21/11/2017 Location: GermanyPosts: 2 |
Great, 2 questions I would have. Would it be possible to turn the clock so that it runs the other way and that is the start pixel on the 6. Almost at LED30.Dann I would provide my LED clock with your sketch and obstruct additionally ne date display. |
||||
| matherp Guru Joined: 11/12/2012 Location: United KingdomPosts: 10953 |
I assume you want this so the wires connect at the bottom? This should be easy to do. Just find all the "pixels.setPixelColor" statements and then change the first parameter by adding 30 modulus 60. e.g. pixels.setPixelColor(hourpos, pixels.Color(0,170,0)); becomes: pixels.setPixelColor((hourpos+30) % 60, pixels.Color(0,170,0)); |
||||
| zoggermaster Newbie Joined: 21/11/2017 Location: GermanyPosts: 2 |
Yeah exact. My clock is build from another instructions (sorry for my Bad English). Changed that and that's how it works. Now the clock only has to turn clockwise ^^. |
||||
| rxmas Newbie Joined: 28/06/2019 Location: United StatesPosts: 1 |
So it took me a couple of days but I finally got this sort of working. I didn't put in the 7 segment displays, I just wanted the ntp and ring clock. My problem is it's running counter clockwise. How do I change the direction? I'm not very good at coding but I know there is a lot of excess code in this sketch so I'm not sure where to even look. I saw the reply to change the position of the 12 oclock, I'm going to need that as well, but the direction has me stumped. Thank you for any help. |
||||
| matherp Guru Joined: 11/12/2012 Location: United KingdomPosts: 10953 |
Try: pixels.setPixelColor(59-tm->tm_sec, pixels.Color(170,0,0)); pixels.setPixelColor(59-tm->tm_min, pixels.Color(0,0,255)); pixels.setPixelColor(59-hourpos, pixels.Color(0,170,0)); and to also move the start point pixels.setPixelColor(59-((tm->tm_sec + 30) % 60), pixels.Color(170,0,0)); pixels.setPixelColor(59-((tm->tm_min + 30) % 60), pixels.Color(0,0,255)); pixels.setPixelColor(59-((hourpos + 30) % 60), pixels.Color(0,170,0)); |
||||
| The Back Shed's forum code is written, and hosted, in Australia. | © JAQ Software 2026 |